Share this handpicked notes of NCERT class 9th Geography Chapter 6 Population growth & Development notes by Vibha Madam to your friends and classmates.
What is the Population?
Population is the total number of people living in a country at a given point of time.
Census
The census is the data collection of the population which provides us with information regarding the population of a country .
- The data provided by the census board, is used by the government for its current and future planning.
- In India the first census was held in the year 1872. The census has been held regularly every tenth year.
- The Indian census is the most comprehensive source of demographic, social and economic data.
Main objectives of studying population
1) Estimate the total manpower available for production
2) The total amount of goods and services required for their consumption
Three major aspects of the population
a) Population size and distribution
b) Population growth and process of population change
c) Qualities of the population
a) Population Size and Distribution
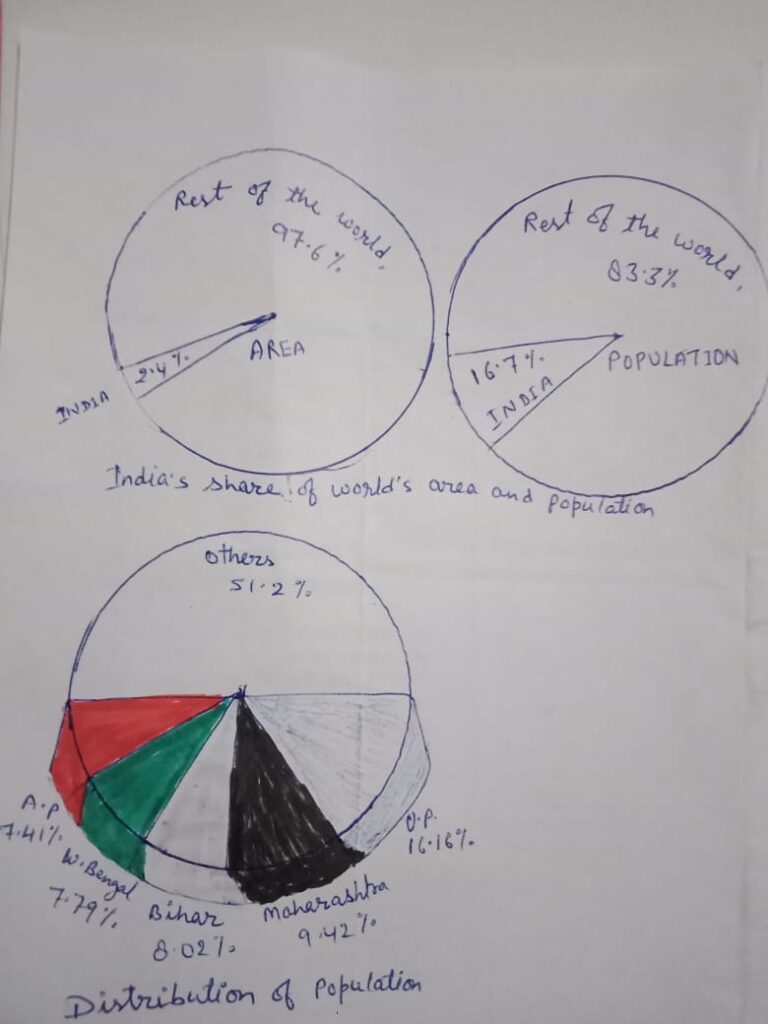
Distribution of population
Population size of UP – 199.6 million people (16.49% of total population of India)
Population size of Sikkim – about 0.5 millions
Highest density of population – Bihar 1102 persons per sq km
Lowest density of population – Arunachal Pradesh :-17 persons per sq km
Density of population – Number of person living per unit of area per sq km)
1) Densely Populated Areas
- More than 400 person living per sq km
- The population is dense due to fertile soil and good rainfall
Areas -Malabar coast, Coastal plains, Satluj and Gangetic plains, Coromandel coast
States -Bihar, Punjab, UP, West Bengal
2) Medium Density Areas
- Population about 200-400 persons living per sq km
- High density is due to coastal regions, industrial regions, ports
Areas -Brahmaputra valley
States – Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, MP, Assam
3) Thinly Populated Areas
- Less than 200 persons living per sq km
- Due to unreliable rainfall and hilly terrain
Areas – Great Indian desert, hills of north- east
States – Kashmir, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim
b) Process of Population Change or Growth
Population growth means change in the number of inhabitants of the country or territory during a specific period of time.
- Birth rate -Number of living birth per thousand persons in a year
- Death rate – Number of death per thousand persons in a year
- Migration – Internal and international migration
- Push factors – Poverty and unemployment
- Pull factors – Employment opportunities, better living conditions, amenities, infrastructures
Sex ratio – It is defined as the number of females per 1000 males.
Occupational structure – The distribution of the population according to different types of occupation is referred as the occupational structure.
a) Primary activity – Goods are produced by exploiting natural resources for example, agriculture, animal husbandry, forestry, fishing, mining
b) Secondary activity – Goods are produced by using simple tools or machines for example, manufacturing industry, building and construction work
c) Tertiary activity – It provides useful services to primary and secondary sectors for example, transport, communication, commerce ,banking, administration
Overpopulation
It is a situation when the resources are too few for the size of population.
This situation arises when a country is not able to maintain a reasonable standard of living for the increased population.
c) Qualities of the Population
Age composition – The population of a nation is generally grouped into three broad categories:-
- Children (generally below 15 years)
They are economically unproductive
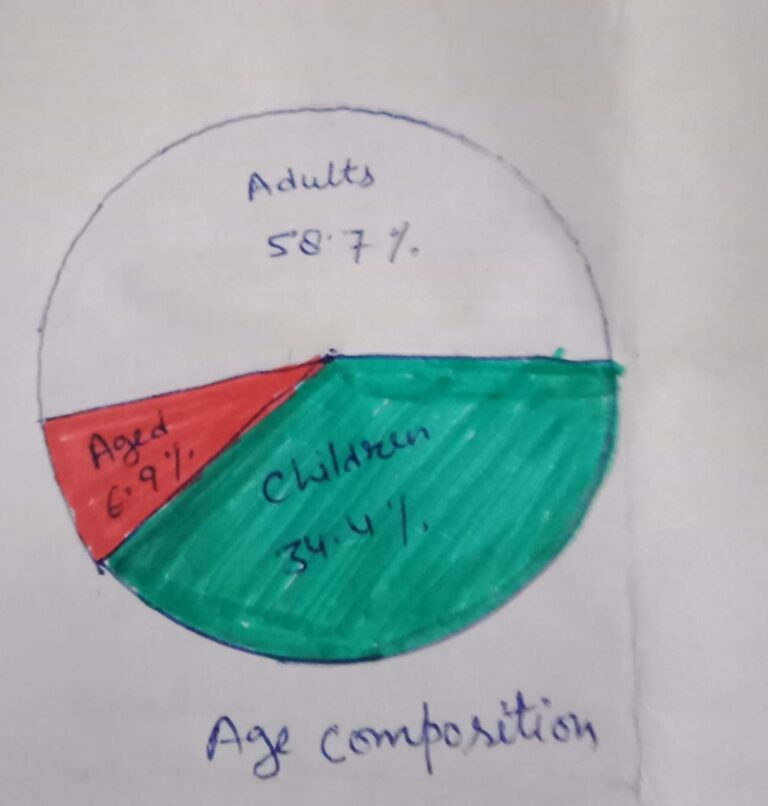
- Working age (15-59 age)
They are economically and biologically reproductive
- Aged (above 59 years) they can be economically productive though they may have retired.
They may be working voluntarily.
Dependency Ratio
The percentage of people depending on the working class is known as dependency ratio. In India below the age of 15 and above the age of 59 years comes under this category.
Cause of higher dependency
a) Very high birth rate &
b) Increase in life expectancy.
Adolescent Population (age from 10 to 19 years)
They currently comprise about 20% of India’s population and an important future resource for the country. Their nutritional requirements are more than other age group
Literacy rate
This is an important quality of the population. Low levels of literacy are an obstacle for economic development.
Health
The health of a population affects its development significantly. High life expectancy, health care, level of nutrition, safe drinking water, proper sanitation are the major indicators of health condition of the population.
National Population policy (NPP)
- First family planning program promoted in 1952
- In 2011, the government formulated the National Population policy.
Major objectives of NPP
- Providing free and compulsory school education up to 14 years of age
- Reducing infant mortality rate
- Achieving universal immunization
- Promoting delayed marriage
- Making family welfare.
FAQ’s
Natural events or calamities become disasters only when they affect a crowded village or town.
A person, 7 years and above who can read and write with understanding in any language.
A quality of population can be measured by age, sex composition, literacy levels, occupational structure and health condition.
Uttar Pradesh
Birth rate, death rate and migration influence the population growth or change of any country.
About one-fifth of the total population.
A healthy and educated population can become a human resource for a country.
138 crore (in year 2020)
The 16th Indian census will be taken in 2022.
Cities with a population of more than 1 million or 10 lakh are called plus cities.
Don’t forget to comment in the comment section below to appreciate the hard work of our author by sharing this notes with your known person you can also Contact us for any query or if you are interested in writing with us.
Stay tuned for more amazing stories, poems & articles like this.




great notes so easy and on point notes
Nice